Champion Dental Clinic is the leading dental clinic in Vietnam for reliable dental examination and treatment. With many years of experience in the field, a team of highly skilled doctors, and modern equipment, Champion Dental Clinic is confident to provide the best services and comprehensive dental care for all clients.
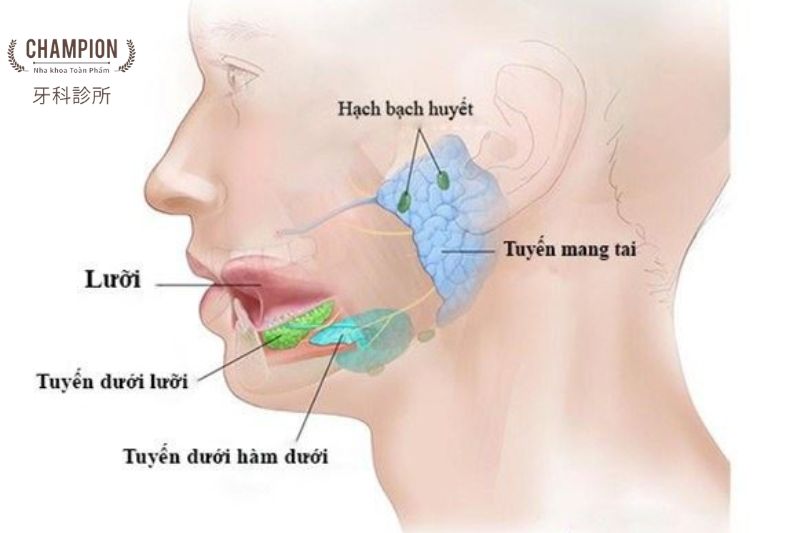
Salivary gland calcification is a condition where calcium salts deposit in the salivary glands, leading to the formation of calcified particles in the glands and salivary ducts. This is considered a common condition in the elderly. So is salivary gland calcification a dangerous disease? And how much should we care about this condition? Let's find out with Champion Dental Clinic right below!
What is salivary gland calcification?
Salivary gland calcification is the accumulation of calcium salts, mainly calcium oxalate and calcium phosphate, in the form of calcified particles in the salivary glands and ducts. When the salivary glands are damaged or infected, calcium salts will precipitate and cause obstructive sialadenitis.
The main cause of salivary gland calcification is an imbalance between calcium and phosphate concentrations in saliva. High calcium or low phosphate levels will lead to calcium phosphate precipitation. In addition, decreased salivary flow also increases the risk of calcium salt deposition.
The stages of salivary stones formation in the glands and ducts occur as follows:
- Stage 1: Salivary gland injury leads to leakage of salts and proteins across cell membranes.
- Stage 2: Increased calcium alters the salivary environment, accelerating the precipitation process.
- Stage 3: Calcium oxalate and calcium phosphate crystals form, accumulating into stones.
- Stage 4: Stones enlarge, causing salivary duct obstruction. Clinical symptoms appear.
Thus, the imbalance of mineral concentrations in saliva combined with gland injury provides conditions for the formation of calcified stones.
Causes of salivary gland calcification
There are several factors that can lead to salivary gland calcification, the most common are:
Due to aging
Salivary gland calcification is common in the elderly as the salivary glands atrophy and have reduced saliva secretion. The elderly also often have impaired calcium and phosphate regulation, increasing the risk of salt deposition.
Due to salivary stones
The presence of stones in the glands causes mucosal injury, leading to leakage of minerals. This is an important factor for new stone formation.
Due to infection
Bacterial or viral infections damage the glands, causing inflammation and altering the salivary environment, enabling calcium salt precipitation.
Due to metabolic disorders
Some diseases increasing blood calcium such as hyperparathyroidism, adrenal cortical fibrosis, also increase the risk of salivary gland calcification.
In addition, a high sugar diet and calcium-phosphate imbalance also contribute to salivary gland calcification.
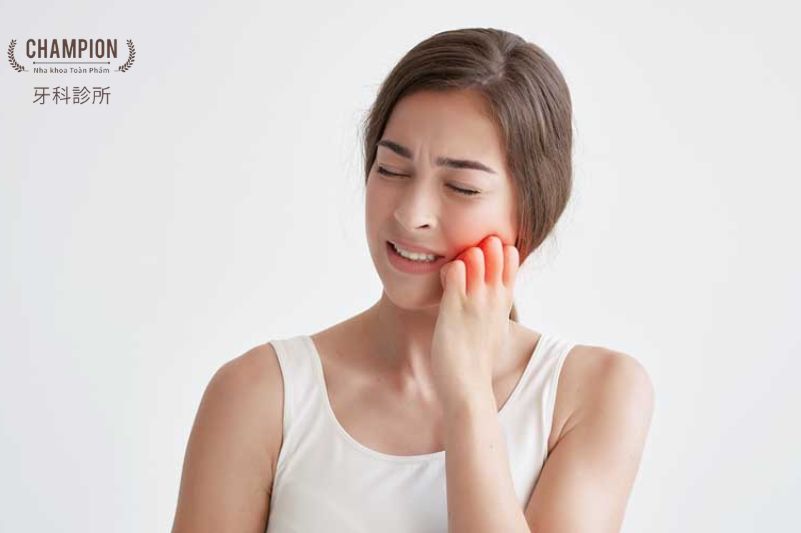

Symptoms of the disease
Salivary gland calcification is a serious condition that directly affects your health. When the salivary glands are calcified, patients often have the following manifestations:
Swelling and pain
The affected salivary gland area will become swollen and painful, causing discomfort in the jaw and ear area. The swelling and pain often gradually increases over time.
Dry mouth and thirst
As the salivary glands are obstructed, reducing saliva secretion, patients often have dry mouth, lack of saliva, and feel thirsty.
Viscous saliva
In late stages, saliva can become dense and mucous due to accumulation of calcium salts. Patients feel their saliva is thick and sticky.
In addition, chronic obstructive conditions can also lead to dangerous complications such as:
- Salivary gland infection or blood infection.
- Salivary stones move and cause airway obstruction.
- Saliva retention causes sinusitis or otitis media.
- Salivary gland cancer (but very rare).
Therefore, if you detect any abnormal signs in the salivary glands, you should visit specialized medical facilities for examination and timely treatment.

Diagnosis of the disease
Necessary examinations and tests to diagnose salivary gland calcification include:
- Clinical examination: check gland swelling, saliva quality.
- X-ray of the facial jaw area: detect stones in glands, measure size.
- CT scan: accurately determine location and extent of lesions.
- Blood test: assess calcium, phosphate levels, thyroid function.
- Saliva test: evaluate composition and physicochemical properties.
- Gland biopsy: take gland tissue samples for histopathological examination.
Early diagnosis helps detect the disease in early stages, thereby having appropriate treatment plans, avoiding dangerous complications.
>> See more: Should Crooked Wisdom Teeth be Extracted? Expert Advice
Treatment methods
Depending on the degree of calcification, doctors can choose appropriate treatments such as:
Medical treatment
Using medicines like antibiotics, pain relievers, anti-inflammatories to control symptoms. Also, adjusting the diet to be rich in vitamins and low in salt.
Surgery
Completely removing the affected gland or removing stones combined with preventive antibiotics.
Laser therapy
Using laser beams to break up stones, unblocking obstructed ducts. This is a minimally invasive method with quick recovery time.
In addition, patients need to practice dental hygiene, rinse mouth to support treatment.
Regular health checks also help detect and intervene promptly if the condition recurs.

Analysis of disease severity
Based on information about the causes, symptoms and complications, salivary gland calcification should be considered a concerning pathology for the following reasons:
- Salivary gland damage causes loss of saliva secretion
- Salivary duct obstruction makes eating, speaking difficult
- Chronic inflammation can spread to nearby organs like ears, nose, throat
- Risk of infection complications, even sepsis
- Risk of septic shock and respiratory failure if stones move to obstruct airways
- Greatly affects quality of life if the condition persists without treatment
- Increased risk of cancer (although very low probability)
Thus, without timely detection and intervention, salivary gland calcification can potentially lead to life-threatening complications.
Therefore, this is considered a pathology that needs serious treatment, avoiding trivialization or complacency. Patients need to fully comply with doctor's instructions and follow-up appointments
Effective prevention tips
To minimize the risk of disease, you should take the following measures:
- Maintain good oral hygiene, brush properly
- Get dental checkups every 6 months to early detect salivary issues
- Limit sweets, sugar, spicy foods that irritate salivary glands
- Supplement a balanced diet with minerals, vitamins
- Avoid smoking, alcohol abuse
- Keep neck warm, avoid upper respiratory illnesses
- Exercise regularly, maintain proper weight
- Treat underlying diseases that increase blood calcium
- Get regular checkups to monitor overall health
Hopefully these tips will help you prevent the disease. Always pay attention to protecting and caring for your oral health!
Conclusion
Salivary gland calcification is a dangerous pathology if not treated properly. The disease can cause many harmful complications, seriously affecting health and quality of life.
Therefore, when there are abnormal signs in the salivary gland area, you should promptly visit reputable medical facilities for examination. Fully comply with treatment regimens and doctor’s advice.
At the same time, applying effective preventive measures can help reduce the risk. Wishing you good health and strong teeth!
Vietnamese & English: (028) 5411-2295
中文: (028) 5411-2297 172 Nguyen Luong Bang, Tan Phu Ward, District 7, Ho Chi Minh City.
Fanpage: Champion Dental Clinic 牙科診所
Zalo: Champion Dental Clinic
Youtube: Champion Dental Clinic 牙科診所
 Champion Dental Clinic
Champion Dental Clinic



