Oral health has a significant impact on a child's overall well-being. Healthy teeth and gums contribute to better eating and speaking abilities. Proper oral care not only protects a child's oral health from an early age but also establishes good habits for their future. Poor oral hygiene habits can lead to dental diseases, infections, and other dental issues.
To help children enjoy and take an active role in oral hygiene, parents can employ the following tips:
- Allow children to choose their toothpaste. Let them select the toothpaste with colors and flavors they prefer. The same applies to choosing a toothbrush.
- Read books or show videos that teach proper oral care and emphasize its importance to children.
- Ensure that children brush their teeth for a full 2 minutes by using a timer or playing their favorite song.
- Encourage children by rewarding their good oral care habits with items they love (not food or sweets), such as apples or stickers.
- Plan enjoyable activities or outings that children look forward to after each dental visit.
- By implementing these tips, parents can foster a positive and proactive attitude towards oral hygiene in children, setting them up for a lifetime of good oral health.
Caring for Children's Oral Health
The role of fluoride
Fluoride plays a crucial role in children's oral health. It helps reduce tooth decay in primary and permanent teeth and strengthens tooth enamel. Most fluoride is present in the water children consume. If the water source does not contain fluoride, children need to supplement it through drinking water. Regularly check your child's oral health to receive advice from a dentist if fluoride supplementation is needed.
During dental visits, children may receive fluoride application, teeth cleaning, or both. Excessive fluoride can contribute to plaque buildup or negatively affect the child's oral health. Therefore, allow the dental professional to assess and provide support regarding fluoride application.
Do not let children swallow toothpaste or fluoride-containing mouthwash. Always follow the guidance of experts on fluoride supplementation for children.

Brushing and dental flossing
Oral care habits should be established when children are young. Start using a soft-bristled toothbrush designed for children when they reach 1-2 years old. It is recommended to brush their teeth with clean water at least twice a day. You can also use a small amount of non-fluoride toothpaste, which is safe for children if swallowed. Remember to use only a pea-sized amount. Teach children how to apply toothpaste to all areas of their mouth, including teeth, gums, and tongue. Consult with a dentist to learn the proper brushing technique for children.
You should assist your child with brushing until they are 7 or 8 years old. At this age, they can use a larger toothbrush. Replace the toothbrush every 1 to 2 months or when the bristles become worn out. Children should brush their teeth for at least 2 minutes each time. Dental flossing is also an important part of daily oral care for children. Teach your child how to use dental floss at least once a day. Choose dental floss with a handle to make it easier for children to use.
You should also teach children how to clean their tongue, which helps reduce bacteria in the mouth.
Tooth Decay
Tooth decay refers to the formation of cavities on teeth. It occurs when bacteria (germs) are present in the mouth. The sugars and carbohydrates in food and drinks convert into acid, which erodes tooth enamel. Tooth decay is more common in children due to difficulties in maintaining oral hygiene. Therefore, each family member should pay extra attention to the oral hygiene of children. Individuals with tooth decay can transmit cavity-causing bacteria to unborn babies, infants, and young children.
Your child may be at risk of tooth decay if they exhibit the following signs:
- Presence of white or brown spots on their teeth.
- Ongoing dental treatments.
- Infrequent dental check-ups.
- Preterm birth or low birth weight.
Dietary Considerations
Children who consume sugary foods or drinks are at a higher risk of tooth decay. It is important to establish healthy eating and drinking habits for children. Limit their sugar intake and reduce fruit juices, sweetened beverages, and soda. Restrict the consumption of snacks and sugary treats between meals. If your child consumes sugary foods, remind them to brush their teeth after eating.
Chewing sugarless gum is safe for older children and may have the following benefits:
- Increases jawbone strength.
- Stimulates saliva production.
- Cleans food debris.
- Neutralizes acid that causes tooth decay.
- However, gum with sugar can contribute to tooth decay. Limit chewing gum with sugar or only allow your child to chew sugarless gum.
Oral Safety Measures
Safety is another important aspect of oral hygiene. If your child participates in sports, they should wear a mouthguard. This can be a soft plastic tray that protects the teeth or, in some cases, a lip guard. These devices help safeguard teeth from injuries. Consult with a dentist if your child requires a custom-fitted mouthguard based on their jaw size.
Tooth Eruption Process
Typically, children begin teething between 4 to 7 months old. The first teeth to erupt are usually the two lower central incisors. By the age of 3, most children have a complete set of 20 primary teeth.
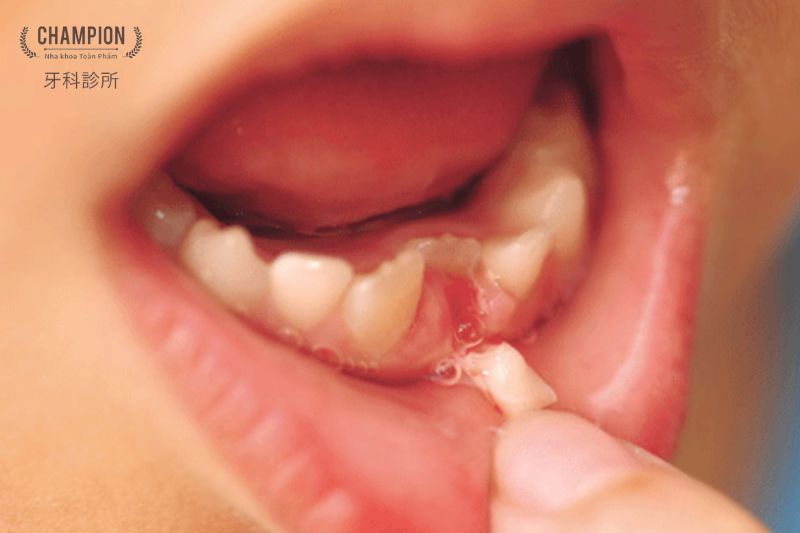
The process of permanent tooth eruption occurs between the ages of 6 to 12. During this phase, the child's primary teeth will shed, making way for permanent teeth to emerge. Dentists can diagnose early oral issues during this period. Some children may require orthodontic treatment, such as braces. A full set of permanent teeth usually consists of 32 teeth, including wisdom teeth. Most people do not experience the eruption of wisdom teeth until adolescence or early adulthood.
Things to Note
Young children often suck their thumb, fingers, or pacifiers. Most children will outgrow this habit by the age of 4. If this habit persists longer, it can affect their teeth. Consult a dentist if your child continues these habits after the age of 4. Dentists can identify any issues your child may be facing. Generally, there is no need to worry if your child maintains these habits until the age of 6.
>> See more: Common Notes for Dental Implant Aftercare
When to Visit the Dentist
The American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry recommends that children should visit a dentist around the age of 1. This early visit helps detect any potential oral issues. The dentist will also guide you on how to properly care for your child's teeth from an early age.
Starting dental visits at a young age will help your child feel more comfortable during future visits. It also establishes a routine of regular dental check-ups for the child. Even adults should have dental check-ups twice a year.
Immediate dental consultation is necessary if:
- Your child experiences toothache or signs of oral infection.
- Your child loses a permanent tooth. If you find the tooth, preserve it in milk and take it to the dentist. They may be able to reattach it.
Questions to Ask Your Pediatric Dentist:
Does my child need fluoride supplements?
What is the best toothbrush for my child?
Can my child use mouthwash?
Is my child at risk of tooth decay?
How often should my child visit the dentist?
Is dental X-ray safe for children?
Is it beneficial for children to chew gum?
Vietnamese & English: (028) 5411-2295
中文: (028) 5411-2297 172 Nguyen Luong Bang, Tan Phu Ward, District 7, Ho Chi Minh City.
Fanpage: Champion Dental Clinic 牙科診所
Zalo: Champion Dental Clinic
Youtube: Champion Dental Clinic 牙科診所
 Champion Dental Clinic
Champion Dental Clinic



